1) xml 파일을 통해 bean 설정하기!
1-1
src/main/resources 안에 xml파일로 만든다
1-2
1-2-1 > xml를 선언해주는 코드를 넣어준다
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN" "https://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd" >
1-2-2 >
<beans> 태그 안에 bean 으로
사용할 id를 적어주고
class에는 dto가 있는 파일경로를 입력해준다
property name="" 변수 명 value 에 값을 입력하면 끝
사용법은 예시 1를 봐주세요
<!-- property태그의 name과 value속성으로 POJO에 대한 값을 지정할 수 있다. -->
<!-- name은 setter메서드가 있어야 동작한다. -->
<!-- 모양은 변수와 같지만 setter가 없으면 인식하지 않는다. -->
<beans>
<bean id="human1" class="com.spring.test.human">
<property name="IQ" value="120"/>
<property name="age" value="30살"/>
</bean>
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN" "https://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd" >
<beans>
<bean id="testManager" class="com.spring.di.TestManager"/>
<bean id="human1" class="com.spring.test.human">
<property name="IQ" value="120"/>
<property name="age" value="30살"/>
</bean>
</beans>
예시1
예시 1-1)
전체 코드 처럼 xml파일을 resuorces폴더안에 만들어 주세요
dto를 하나 만들어준다, getter , setter 를 만들어준다
public class human {
String IQ = "1";
String age = "1살";
public String getIQ() {
return IQ;
}
public void setIQ(String iQ) {
IQ = iQ;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
}예시 1-2)
자바파일을 하나 더만들어 위에 만든 코드를 import하고 getter setter를 만든다 확인할 메소드를 만들어도 좋다
public class TestManager {
Human human;
public Human getHuman() {
return human;
}
public void setHuman(Human human) {
this.human = human;
}
public void print() {
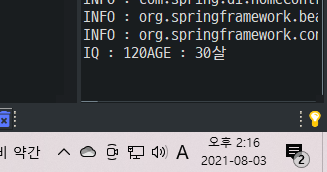
System.out.println("IQ : " + human.IQ + "AGE : "+ human.age );
}
}예시 1-3)
새로 자바파일을 만들어주고
@controller의 권한을 주고
ApplicationContext context = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:test.xml");
("") 안에 classpath 는 resources 파일안을 검색하고 그안에 test.xml파일을 가져오는 것이다
TestManager testManager = (TestManager)context.getBean("testManager");
Human human1 = context.getBean("human1",Human.class);
위에 선언한 2개의 문법은 같은 문법인데 저렇게 두가지로 쓸 수 있다 예를 들어 아래 처럼 사용이 가능하다
context.getBean("testManager",TestManager.class);
@Controller
@RequestMapping("tt")
public class test {
@RequestMapping(value = "/test1" , method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String print() {
ApplicationContext context = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:test.xml");
TestManager testManager = (TestManager)context.getBean("testManager");
Human human1 = context.getBean("human1",Human.class);
testManager.setHuman(human1);
testManager.print();
return "home";
}
}
결과는

'몰아 넣기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA/Spring]<beans:constructor-arg> 사용하기 (0) | 2021.08.03 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA/Spring] @Autowired ,@Inject , @Resource 사용하기 (0) | 2021.08.03 |
| [JAVA/Spring/MyBatis]동적 쿼리문이란? (0) | 2021.07.29 |
| [JAVA/Spring/MyBatis] resultMap 이란? (0) | 2021.07.28 |
| apache-tomcat 설치 및 설정 (0) | 2021.07.28 |